

With age, our discs increasingly lose the ability to reabsorb fluid and become brittle and flatter this is why we get shorter as we grow older. This fluid is absorbed during the night as you lie down and is pushed out during the day as you move upright. The gel-filled nucleus contains mostly fluid. The nucleus acts like a ball bearing when you move, allowing the vertebral bodies to roll over the incompressible gel. The crisscrossing fibers of the annulus pull the vertebral bones together against the elastic resistance of the gel-filled nucleus. The annulus pulls the vertebrae bones together against the resistance of the gel-filled nucleus.ĭiscs function like coiled springs. Discs are made of a gel-filled center called the nucleus and a tough fibrous outer ring called the annulus. While vertebrae have unique regional features, every vertebra has three functional parts (Fig. Together with the iliac bones, they form a ring called the pelvic girdle.Ĭoccyx region - the four fused bones of the coccyx or tailbone provide attachment for ligaments and muscles of the pelvic floor.

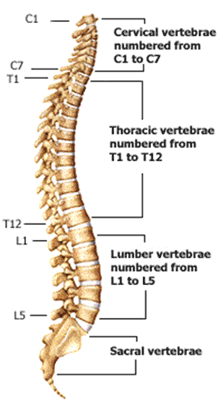
There are five sacral vertebrae, which are fused together. Sacrum - the main function of the sacrum is to connect the spine to the hip bones (iliac). These vertebrae are much larger in size to absorb the stress of lifting and carrying heavy objects. The five lumbar vertebrae are numbered L1 to L5. Lumbar (low back) - the main function of the lumbar spine is to bear the weight of the body. The range of motion in the thoracic spine is limited. The twelve thoracic vertebrae are numbered T1 to T12. Thoracic (mid back) - the main function of the thoracic spine is to hold the rib cage and protect the heart and lungs.

This joint allows for the side-to-side or “no” motion of the head. The second vertebra (C2) is the peg-shaped axis, which has a projection called the odontoid, that the atlas pivots around. This joint allows for the nodding or “yes” motion of the head. The first vertebra (C1) is the ring-shaped atlas that connects directly to the skull. The neck has the greatest range of motion because of two specialized vertebrae that connect to the skull. The seven cervical vertebrae are numbered C1 to C7. The vertebrae in each region have unique features that help them perform their main functions.Ĭervical (neck) - the main function of the cervical spine is to support the weight of the head (about 10 pounds). Only the top 24 bones are moveable the vertebrae of the sacrum and coccyx are fused. The vertebrae are numbered and divided into regions:Ĭervical, thoracic, lumbar, sacrum, and coccyx (Fig. Vertebrae are the 33 individual bones that interlock with each other to form the spinal column. Misalignment puts incredible strain on the spine (see Exercise for a Healthy Back). Something as common as poor muscle tone or a large belly can pull your entire body out of alignment. These muscles enable us to flex, or bend forward, and are important in lifting and controlling the arch in the lower back. The flexor muscles are in the front and include the abdominal muscles.
The extensors are attached to the back of the spine. The extensor muscles enable us to stand up and lift objects. The two main muscle groups that affect the spine are extensors and flexors. An abnormal curve from side-to-side is called scoliosis.An abnormal curve of the thoracic spine is kyphosis, also called hunchback.An abnormal curve of the lumbar spine is lordosis, also called sway back.Excess body weight, weak muscles, and other forces can pull at the spine's alignment: Good posture involves training your body to stand, walk, sit, and lie so that the least amount of strain is placed on the spine during movement or weight-bearing activities (see Posture). The abdominal and back muscles maintain the spine's natural curves.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
