
Osirix md crack crack#
Histologic fatigue damage was not significantly correlated with crack dimensions determined by CT or extensometer micromotion.
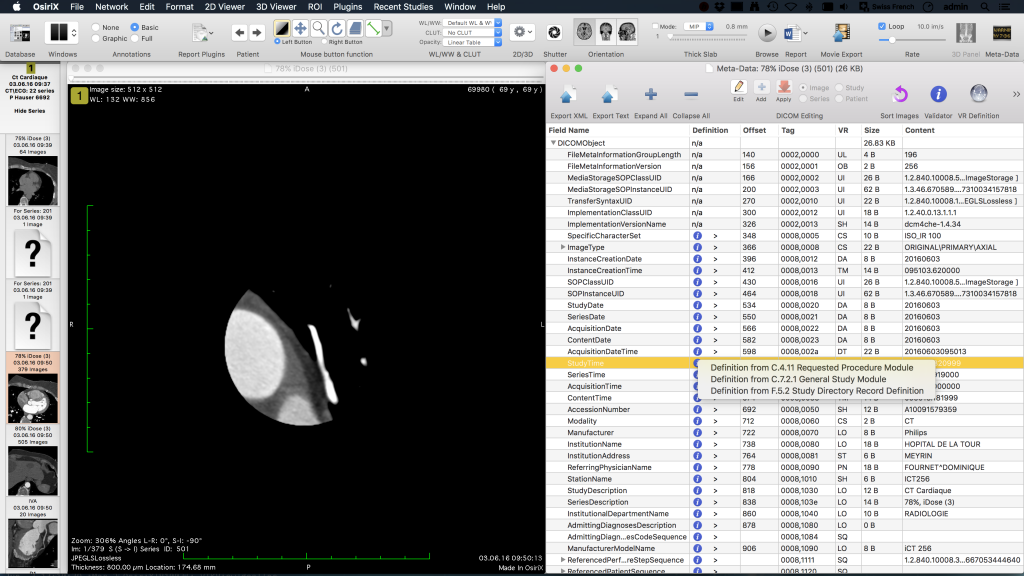
Correlations with transverse and frontal plane crack lengths were not significant. In our biomechanical model, we found a significant positive correlation between extensometer micromotion and parasagittal crack area derived from reconstructed CT images (S R = 0.32, p<0.05). Creation of parasagittal subchondral slots induced significant micromotion during loading ( p<0.001). After testing, subchondral crack density was determined histologically. Mechanical testing was validated using bones with 3 mm and 5 mm deep parasagittal subchondral slots that modeled naturally occurring fatigue cracks. Crack motion was recorded using an extensometer. MC3 bones with fatigue cracks were tested using five cycles of compressive loading at -7,500N (38 condyles, 18 horses). Parasagittal subchondral fatigue crack dimensions were measured on CT images using image analysis software. Limbs were radiographed and examined using CT.
Thoracic limbs from 40 Thoroughbred racehorses that had sustained a catastrophic injury were studied. Using this model, we determined the relationship between subchondral crack dimensions measured using computed tomography (CT) and crack micromotion. We describe an ex-vivo biomechanical model in which we measured subchondral crack micromotion under compressive loading that modeled high speed running. Currently, there is no method for predicting fracture risk clinically. Articular stress fracture arising from the distal end of the third metacarpal bone (MC3) is a common serious injury in Thoroughbred racehorses.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
